World Hepatitis Action Day 2023: "I'm not delaying, I'm taking action!"
In the global fight against viral hepatitis, World Hepatitis Day on July 28, 2023, serves as a significant reminder of the importance of prevention, diagnosis, and treatment. This year's theme, "I don't wait. I act!", encourages the world to take action against this potentially deadly disease.
Viral hepatitis, one of the most common infectious diseases globally, can lead to chronic liver inflammation, liver cirrhosis, or liver cancer. It can be contracted through active or past drug use, receiving blood products before 1992, or having infected sexual partners.
The World Health Organization (WHO) and Dr. Magnus Jung, the Minister of Health of Saarland, are advocating for ambitious elimination targets. The goal is to reduce new hepatitis infections by 90% and mortality by 65% by 2030.
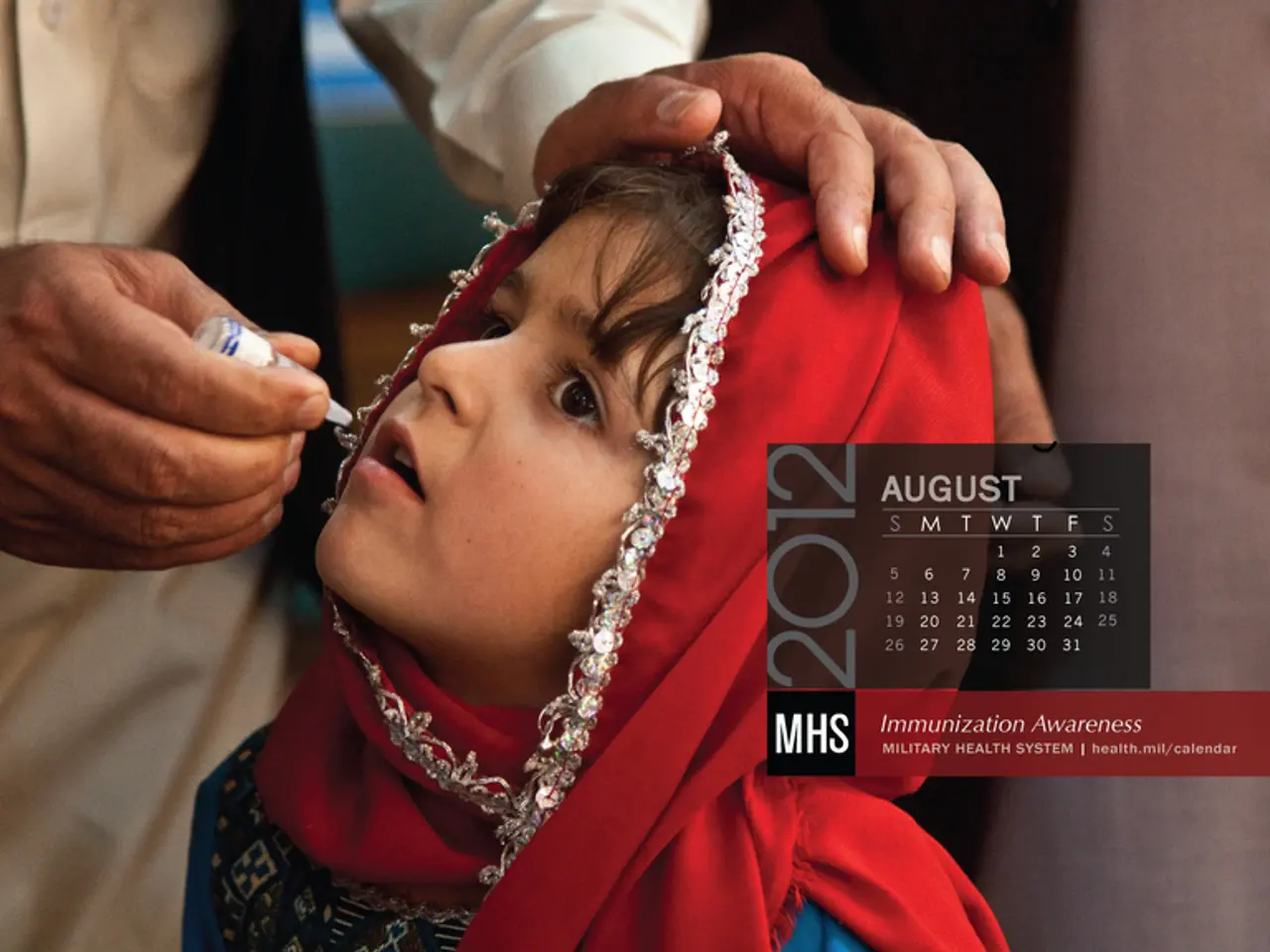
Achieving and maintaining high coverage of the hepatitis B vaccine, particularly the three-dose series for infants, is essential. Over 90% global infant vaccination coverage is targeted, with urgent focus on timely birth doses to prevent mother-to-child transmission.
Many people living with hepatitis remain unaware of their infection. Early diagnosis through widespread testing is critical to enable timely linkage to care and treatment, preventing disease progression and liver cancer development.
Expanded access to antiviral therapies, especially Direct-Acting Antivirals (DAAs) for hepatitis C and antiviral treatment for hepatitis B, is vital. The 2023 WHO treatment guideline updates streamlined clinical protocols to enhance treatment accessibility.
Integrating hepatitis services into primary care and national health systems is emphasised to ensure sustained delivery of prevention, testing, and treatment services. The WHO's 2025 guidance promotes an integrated person-centred strategy to eliminate mother-to-child transmission of HIV, syphilis, and hepatitis B.
Continuous political will, funding, and solidarity are required to embed hepatitis elimination into national health plans, ensure smart investment, and overcome systemic and social barriers that impede service delivery. The role of international partners like Gavi, UNICEF, and others is central in scaling up vaccination and care programs.
Dr. Magnus Jung, as a WHO-affiliated health leader, supports these comprehensive strategies, emphasising the necessity of coordinated global action, integration of hepatitis programming into existing health systems, and prioritisation of vulnerable populations to meet the 2030 elimination goals effectively.
For those aged 35 and above, who are insured by statutory health insurance, testing for hepatitis B and C is available for free as part of the "health check-up". Specialized medical advice can help prevent serious health consequences from long-term, undetected chronic hepatitis infections.
With the right medication, chronic hepatitis C can be completely cured. Patients with chronic hepatitis B can be treated with antiviral drugs to reduce the risk of subsequent diseases and contain the spread of the virus.
In conclusion, the WHO and Dr. Jung endorse a multi-pronged approach: widespread hepatitis B vaccination with timely birth doses, expanded testing and early diagnosis, improved treatment access with updated guidelines, integrated mother-to-child transmission elimination programs, and sustained political and financial commitment, all embedded within national health systems to achieve viral hepatitis elimination by 2030.
- Science plays a crucial role in the development of therapies and treatments for medical-conditions like chronic diseases, such as viral hepatitis, as evidenced by the ongoing advancements in Direct-Acting Antivirals (DAAs) for hepatitis C and antiviral treatment for hepatitis B.
- To ensure health-and-wellness for all, it's important to prioritize fitness-and-exercise, mental-health, and nutrition alongside disease prevention and treatment programs, creating a comprehensive approach to global health.
- Nutritional guidance and balanced diets may aid in the recovery of individuals affected by chronic hepatitis infections, contributing positively to their overall health-and-wellness and reducing the risk of associated complications.
- As chronic diseases such as viral-hepatitis can have long-term effects on mental-health,integrating mental-health services into healthcare programs for these conditions becomes essential for providing holistic therapies-and-treatments to those affected.