Throat Cancer: Signs, Visual Representations, Origins, and Recovery Strategies
**Throat Cancer: Understanding Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment**
Throat cancer, a type of head and neck cancer, can develop in various regions of the throat, each with distinct symptoms and treatment pathways. The most common types include oropharyngeal, hypopharyngeal, laryngeal, and HPV-related throat cancer.
**Types of Throat Cancer**
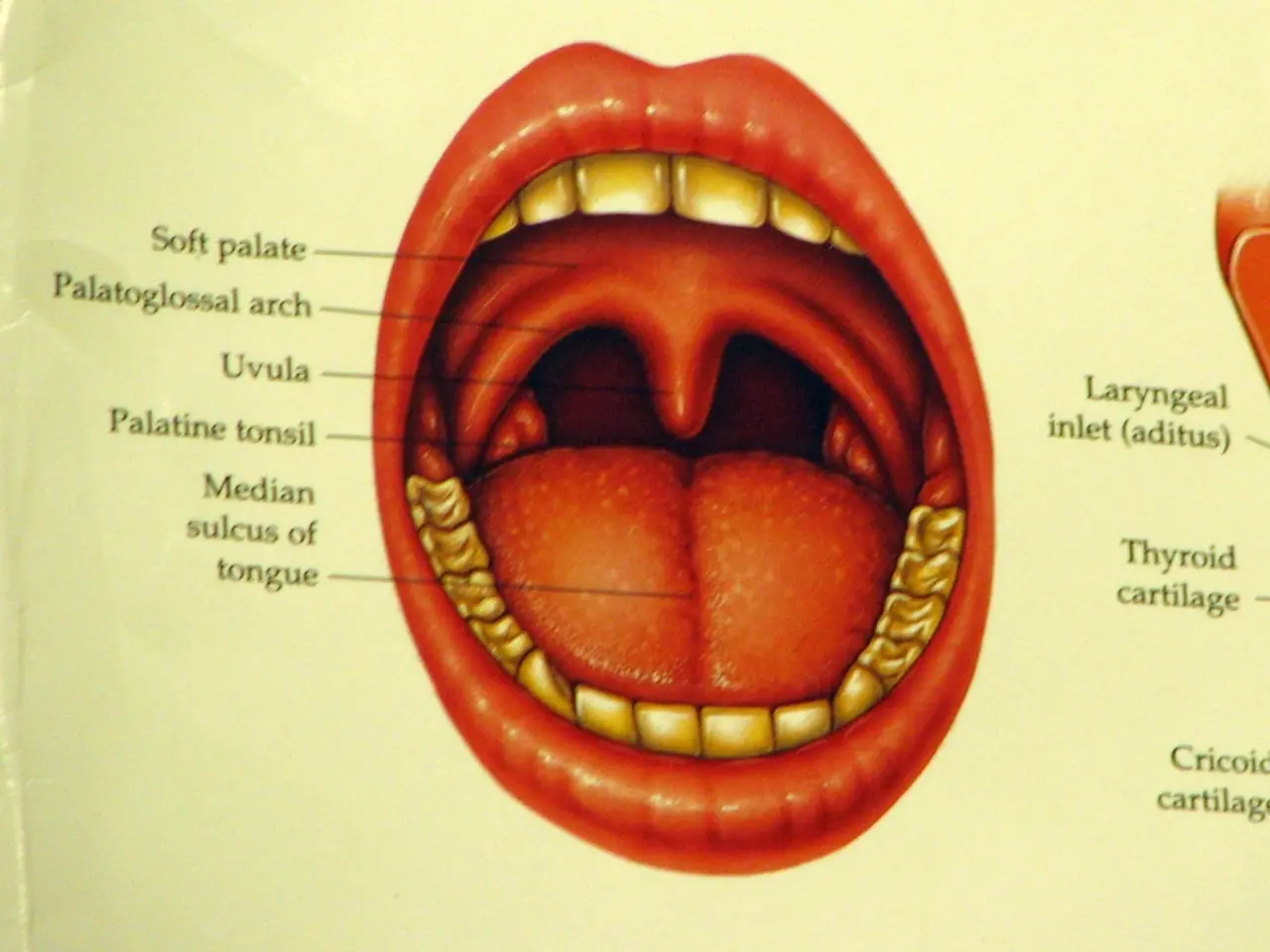
- **Oropharyngeal Cancer:** Affecting the upper part of the throat, this cancer can manifest in the soft palate, tonsils, and base of the tongue. - **Hypopharyngeal Cancer:** Originating in the lower part of the throat, near the windpipe and esophagus. - **Laryngeal Cancer:** Developing in the voice box (larynx). - **HPV-Related Throat Cancer:** Primarily affecting the oropharynx, often linked to human papillomavirus (HPV) infection, especially HPV type 16. This type is increasingly seen in younger, non-smoking individuals and generally has a better prognosis.
**Common Symptoms**
| Cancer Type | Common Symptoms | |---------------------|-------------------------------------------------------------| | Oropharyngeal | Sore throat, difficulty swallowing, changes in voice, ear pain, lump in neck, frequent nosebleeds (when associated with nasopharynx involvement, though nasopharynx is technically different)[2][4]. | | Hypopharyngeal | Hoarseness, throat discomfort, ear pain, difficulty swallowing, weight loss due to dysphagia[2][4]. | | Laryngeal | Persistent hoarseness, voice changes, trouble breathing, lump in the neck[1][4]. | | HPV-Related | Similar to oropharyngeal, but may present in younger non-smokers, often with a neck mass[4]. |
Additional general symptoms may include changes in taste, problems chewing, dry mouth, neck stiffness, and fibrosis (build-up of fibrous tissue impairing function)[2].
**Diagnosis and Staging**
A doctor may use a laryngoscope, imaging tests, and a biopsy to diagnose throat cancer. The staging for throat cancer is used to determine the extent of the cancer and the best treatment method. Stages range from Stage 0 (earliest) to Stage 4 (most advanced).
**Treatment Options**
Treatment depends on the location, stage, and type of throat cancer, as well as the patient's overall health. Options may include surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, targeted therapy, immunotherapy, or a combination of these. HPV-related oropharyngeal cancers usually respond well to treatment and often have a better prognosis.
**Key Points**
- Early-stage tumors (Stage 1 and 2) are generally smaller and localized, with better survival rates. - Advanced-stage tumors (Stage 3 and 4) involve deeper tissues, lymph nodes, and possibly distant organs, requiring more aggressive therapy. - Metastatic or unresectable cancer is more challenging to treat and may focus on symptom control and improving quality of life.
Early detection and prompt treatment are crucial for improving outcomes in all types of throat cancer. Regular follow-ups after treatment are essential to monitor progress and check for recurrence or new cancer. The grade of the cancer affects treatment and outlook, with high-grade cancer being more aggressive.
It is estimated that in 2025, there will be around 13,020 new cases of throat cancer and around 3,910 deaths due to the disease. The 5-year relative survival rate for people diagnosed with throat cancer between 2012 and 2018 varies depending on the location and stage of the cancer, with rates ranging from 45% to 77%.
People with throat cancer may experience side effects from treatment, and should discuss management strategies with their doctor. Clinical trials may offer access to new treatments not yet widely available. A person's doctor is best suited to evaluate their specific outlook in the context of their diagnosis, medical history, and treatment plan.
- In the realm of medical-conditions and chronic-diseases, understanding skin-care is crucial for those dealing with aq eczema, a chronic inflammatory skin disorder.
- The science behind CBD has shown promising effects in managing some neurological-disorders, such as mental-health issues like bipolar disorder.
- Predictive analysis in health-and-wellness can help identify individuals at risk for certain cancers, providing them the opportunity for early intervention.
- Fitness-and-exercise plays a significant role in maintaining overall wellness and potentially reducing the risks of various chronic-diseases, including certain cancers.
- Nutrition is key in managing not only aq eczema but also other medical-conditions, ensuring the body receives essential nutrients.
- When it comes to treating cancer, medical professionals employ a variety of approaches, including surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, targeted therapy, immunotherapy, or a combination of these treatments.
- Early detection and proper management of cancer, like throat cancer, are vital in preventing the development of more severe aq neurological-disorders or other chronic-diseases.